IP
1. IP地址
ip地址按照目的地分,可以分为unicast,anycast,multicast,broadcast四种。
分类寻址(classful addressing)
最开始ip地址划分为五个段。
| Class | Address Range | High-Order Bits | Use | Fraction of Total | Number of Nets | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.0.0.0–127.255.255.255 | 0 | Unicast/special | 1/2 | 128 | 16,777,216 |
| B | 128.0.0.0–191.255.255.255 | 10 | Unicast/special | 1/4 | 16,384 | 65,536 |
| C | 192.0.0.0–223.255.255.255 | 110 | Unicast/special | 1/8 | 2,097,152 | 256 |
| D | 224.0.0.0–239.255.255.255 | 1110 | Multicast | 1/16 | N/A | N/A |
| E | 240.0.0.0–255.255.255.255 | 1111 | Reserved | 1/16 | N/A | N/A |
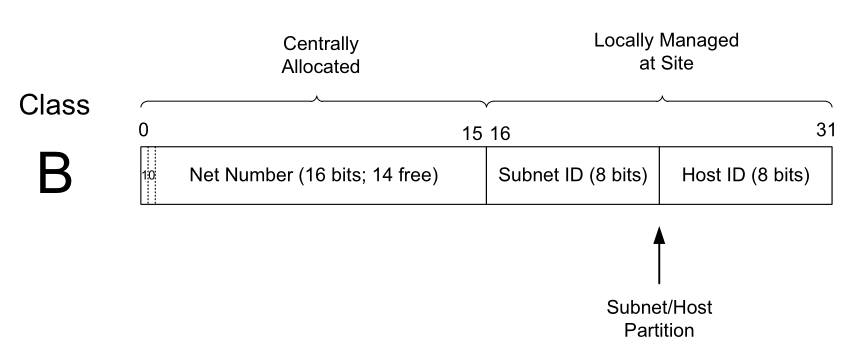
子网寻址(subnet addressing)
互联网飞速发展,传统将IP地址分为A,B,C类也暴露了扩展问题(scaling problems),对新加入的网络分配很难确定应该分配A还是B,特别对发展迅速的公司。
于是出现一种可以让当地管理员(site administrator)对网络段进行进一步的划分,并且不影响其它网络的方法,这就是子网寻址。因为子网选址只对本地网络可见,所以不会影响ip地址路由机制。子网寻址带来灵活性的同时,也增加了额外的消耗,每个路由器和主机都需要通过子网掩码识别子网。
可变长度子网掩码
可变长度子网掩码 Variable-length subnet masks (VLSM):支持不同子网管理不同数量的主机。VLSM,需要路由器运行动态路由协议(OSPF,IS-IS,RIPv2)。
CIDR和聚合
CIDR(Classless Inter-Domain Routing),提供了一种便捷分配255-65535的连续地址空间的方法。CIDR掩码不仅site可见,而是全路由系统可见。
特殊地址
部分特殊地址:
| Prefix | Special Use | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0.0.0/8 | Hosts on the local network. May be used only as a source IP address. | [RFC1122] |
| 10.0.0.0/8 192.168.0.0/16 172.16.0.0/12 | 局域网地址 | [RFC1918] |
| 127.0.0.0/8 | Internet host loopback addresses (same computer). Typically only 127.0.0.1 is used. | [RFC1122] |
| 169.254.0.0/16 | “Link-local” addresses—used only on a single link and generally assigned automatically. See Chapter 6. | [RFC3927] |
| 192.88.99.0/24 | Used for 6to4 relays (anycast addresses). | [RFC3068] |
| 224.0.0.0/4 | 组播地址(multicast addresses),只当做目的地址. | [RFC5771] |
| 240.0.0.0/4 | Reserved space (formerly class E), except 255.255.255.255. | [RFC1112] |
| 255.255.255.255/32 | Local network (limited) broadcast address. | [RFC0919] [RFC0922] |
任播地址(Anycast Addresses):就是一个unicast地址,它会根据所在不同的网络,标示不同的主机。This is accomplished by configuring Internet routers to advertise the same unicast routes from multiple locations in the Inter。
通常用来找到最合适的主机,比如找寻DNS server,同一个8.8.8.8地址,会返回最近的dns server。 net
2. 广播和多播
广播地址和多播地址一般用于用于UDP和ICMP。
广播
路由器copy消息以向多个主机发送消息。如果主机在一个本地网络中,由链路层做广播。
链路层的广播地址,ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
广播地址,主机地址全部设置成1。使用这种地址当做目的地的数据包,被称作定向广播(directed broadcast)。但因为安全原因,被禁用。
API向广播地址发送消息的时候,需要带上SO_BROADCAS标示
255.255.255.255,有限广播地址,但是并没有形成标准,应该由哪个interface发送。所以是操作系统,
可以用路由表来确定哪个interfaces用来做广播。
# -b 运行使用广播地址,windows不用在-b
Linux# ping –b 10.0.0.127
组播(Multicast)
组播多用于本地网络。组播需要主机和路由器保存multicast stat,只会对组内成员发送消息。作为软状态(soft state)。如果没有及时刷新,状态就会被删除。
组播地址可以表示一组的电脑。组的范围包括node-local(同一电脑),link-local(同一子网),site-local,global(整个internet)和administrative(在路由器手动配置)。
224.0.0.0–239.255.255.255的保留地址用作组播地址。并被分做多个用途。详细见tcpip详解
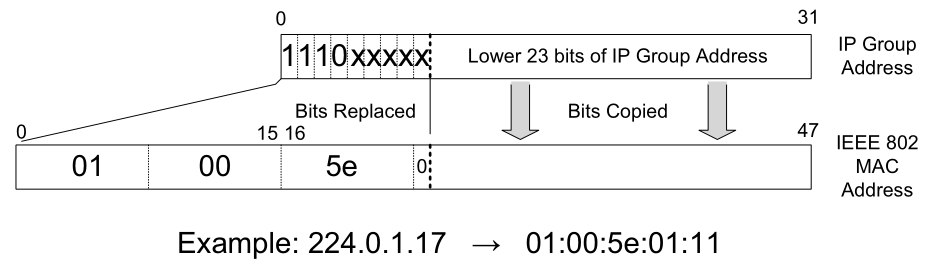
不同厂商拥有一段链路层地址。IANA将它的一些地址空间用作支持IP multicasting。01:00:5e:00:00:00 - 01:00:5e:7f:ff:ff
ip多播地址会将表示组的23bit拷贝到对应的链路层地址上。因为组id的地址有28位,这个映射不是一一对应的,多个组id会映射成同一个链路地址。
最小的跃点数(metric),就是优先用作组播的interface。
$> netstat -rn
IPv4 路由表
===========================================================================
活动路由:
网络目标 网络掩码 网关 接口 跃点数
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 在链路上 127.0.0.1 331
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 在链路上 192.168.101.82 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 在链路上 169.254.238.12 281
#linux可以用netstat –gn
$> netsh interface ip show joins
接口 12: 以太网 2
作用域 参照 上一次 地址
---------- ---------- ---- ---------------------------------
0 0 是 224.0.0.1
0 6 是 224.0.0.251
0 1 是 224.0.0.252
0 1 是 230.0.0.1
0 0 是 239.192.152.143
0 3 是 239.255.255.250
